Glossary - Part C
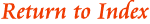
• Caisson: A water tight metal cylinder placed in a shallow water area ad used as the base of an off-shore lighthouse structure.
• Caisson Style Tower: Lighthouse built on an iron caisson. A caisson was essentially a hollow tube made of heavy rolled-iron plates.
• Candela: The Standard International Unit of measurement for luminous intensity.
• Candlepower: Luminous intensity (brightness) as measured in units called candles.
• Cast-iron Tower: Usually cylindrical in shape, these lights became popular in the 1840’s.
• Catoptric: A light which uses a concave mirror for magnification.
• Catwalk: A narrow elevated walkway, allowing the keeper access to light towers built out in the water.
• Chandelier: In lighthouses, a circular fixture suspended from the ceiling that holds a number of lamps or light bulbs.
• Channel aids to navigation: Pilings or buoys used to indicate the edges of a channel.
• Characteristic of a light: In a lighted aid to navigation the characteristic identifies a particular aid from those in proximity. Fixed or flashing lights as well as colors help the mariner distinguish aids that are in proximity to each other. Characteristics include occulting, group flash, equal interval, etc.
• Chariot: The wheeled carriage at the bottom of a Fresnel lens assembly, which allowed the lens to rotate around a circular iron track atop the lens pedestal.
• Cistern: A receptacle or tank for collecting and holding water or other liquid.
• Clamshell Lens: Rather than being round as most lenses are the Clamshell, or Bivalve, lenses has a flattened shape reminiscent of a clamshell. They usually have two bull's-eyes, one on each side of the lens.
• Clockwork Mechanism: The mechanism that turned the light in early lighthouses. They were made up of a series of gears, pulleys and weights, which had to be wound periodically by the keepers.
• Coastal Light: A medium sized lighthouse marking major coastal features such as capes, points and major islands.
• Collector of Customs: The person employed to collect the duties or taxes imposed on imported and, less commonly, exported goods. Some collectors also served as superintendent of lighthouses.
• Commissioned: The action of placing a previously discontinued aid to navigation back in operation.
• Composite Group Flashing Light: A group-flashing light in which the flashes combined in successive groups of different numbers of flashes.
• Composite Group Occulting Light: A light similar to a group-occulting light except that the successive groups in a period have different numbers of eclipses.
• Concrete Octagonal: Eight sided tapering tower made of concrete, which continues a traditional wooden style in a more permanent material.
• Condensing Lens: A means by which radially dispersed light from a single light source is concentrated into a beam.
• Conical Rollers: Lens Rollers made in the form of truncated cones used to assist the movement of a rotating lens by reducing friction.
• Coordinates: The latitude and longitude of a lighthouse.
• Cornice: Ornamental overhang often found on lighthouses as a graceful decorative treatment below the lantern or gallery deck.
• Cottage Style Lighthouse: A lighthouse comprised of a small one story building with a light on top that housed the keeper(s).
• Cupola Style: A structure with the lantern rising from the center of the dwelling.
• Crib: A structure, usually of timbers, that was sunk in water through filling with stone, and served as the foundation for a concrete pier built atop it.
